Können Tiere sprechen? Hat ihre Kommunikation Eigenschaften menschlicher Sprache? Haben wir Zugänge? Was ist der Mensch - ein Sprachwesen? Denken wir in sprachlichen Kategorien? Ist Lernen sprachlich? Ist das
autobiographische Gedächtnis menschentypisch? Inwieweit versetzen
wir uns in Andere? Wie kommunizieren Elefanten, Ameisen, Grillen, Delfine, Wale? |
 |
"Ein Hund könnte lernen (Ludwig Wittgenstein, |
letzte Bearbeitung: 22.04.2022
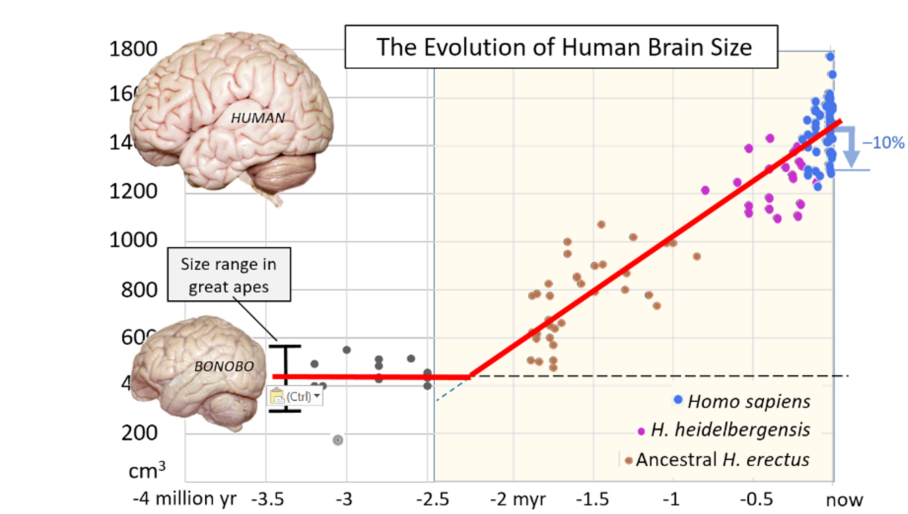
Quelle: William Calvin: http://www.williamcalvin.com
Handbuch
*Bohlen, E./Thies, C. (Hg.)(2009) Handbuch Anthropologie. Stuttgart: Metzler [Klassiker, Ansätze, Begriffe der Anthropologie]
*Thallerman, M./Gibson, K-R. (eds.)(2011) The Oxford Handbook of Language Evolution. Oxford: University Press
Primatenkommunikation,
Biolinguistik
*Antweiler,
C. (2007) Was ist den Menschen gemeinsam? Über Kultur und Kulturen.
Darmstadt: Wiss. Buchgesellschaft
*Arbib, M. (2012) How the Brain Got Language. Oxford: University Press
Armstrong, D./Karchme. A. /Vickery Van Cleve, J. (eds)(2006) The study of signed languages: Essays in honor of William C. Stokoe.Washington D.C.: Gallaudet University Press
Armstrong, D./Wilcox, S.E. (2007)
The gestural origin of language. Oxford: University Press
Bannan, M. (ed) (2012) Music, Language, and Human Evolution. Oxford: University Press
Bekoff, M., Jamieson, D. (1990) Readings in animal cognition. Cambridge, Mass.:
MIT Press.
Berwick, R. C./A. D. Friederici/N. Chomsky/J.J. Bolhuis (2013) Evolution, brain, and the nature of language. In: Trends in Cognitive Sciences February 2013, Vol. 17, No. 2
Byrne, R. (1995) The thinking ape. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Botha, R./Everaet (eds) (2013) The Evolutionary Emergence of Language. Oxford: University Press
Bourne, G. H. (ed.) (1977) Progress in Ape Research. New York: Academic Press
*Brandt, R. (2009) Können Tiere denken? Frankfurt: Suhrkamp
*R. Burling (2005) The Talking Ape. Oxford: University Press
Call, J./Tomasello, M. (2008) Does the chimpanzee have a theory
of mind? 30 years later. In: Trends in Cognitive Sciences 12, 187-192
Chauvin R./Muckensturm-Chauvin, B. (1980) Behavioural complexities. New
York: International Universities Press.
Chomsky, N. (1980) Human language and other semiotic systems. In: Seboek, Th.A.
/ Umiker-Seboek, J. (eds.): Speaking of Apes: A Critical Anthology of Two-Way
Communication with Man. New York: Plenum Press, 429-440
Chomsky, N./Hauser, M.D./Fitch, W.T. (2003), The Faculty of Language: What Is It, Who Has It, and How Did It Evolve? In: Science, VOL 298, 2002, 1569-1579
*Christiansen, M.H./Kirby, S. (eds.)(2003) Language Evolution. Oxford: University Press
Christiansen, M.H./Collins, C./Edelman,
S. (2009) Language Universals. Oxford: University Press
M. Christiansen/N. Chater (2022) The Language Game.
How Improvisation Created Language and Changed the world. London: Bantam
Press
Cole, J. (1989). Animal Communication: Opposing View Points. St Paul:
Greenhaven Press
*Conard, J.N. (ed.)(2006/2) Wher kommt der Mensch? Tübingen: Attempto
Corballis, M. C. / Lea, S. E. G. (eds.) (1999). The descent of mind. Oxford University Press
Corballis, M.C. (2002) From Hand to Mouth:
the origins of language. Princeton: Princeton University Press
de Luce, J. and Wilder, H.T. (eds.) (1983) Language in Primates: Perspectives
and Implications. New York: Harper Collins Publishers.
Desalles, J.L. (2007) Why We Talk. The Evolutionary Origins of Language. Oxford:
University Press
Domjan, M. / Burkhardt, B. (1986) The Principles of Learning and Behaviour. Brooks-Cole
Dor, D./Knight,C./Lewis, J.(eds)(2014) The
Social Origins of Language. Oxford: UP
*Dunbar, R. (1996) Klatsch und Tratsch. München: Bertelsmann
*Duncker, H.-R. (2006)
Vorstellungen zu einer aktuellen Anthropologie aus biologisch-medizinischer
Sicht. In: Duncker, H.-R. (Hg.) Beiträge zu einer aktuellen Anthropologie. Zum
100jährigen Jubiläum der Gründung der Wissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft
im Jahre 1906 in Straßburg. Stuttgart: Franz Steiner Verlag, 12-22
*Dupré,
J. (2005) Darwins Vermächtnis. Frankfurt: Suhrkamp
*Enard, W. (2010) Menschwerdung II - Die Auskunft der Genome.
In: Fischer, E.P./Wiegandt, K. (2010), 57-74
*D.
Everett (2005) Cultural Constraints on Grammar and Cognition in Piraha.
In: Current Anthropology Volume 46, Number 4, August–October 2005
D. Everett (2013) Die größte Erfindung der Menschheit. Was mich meine Jahre am Amazonas über das Wesen der Sprach gelehrt haben. München: DVA [Orig. 2012: Language. The Cultural Tool. New York: Pantheon]
D. Everett (2017) How Language Began: The Story of Humanity's Greatest Invention. London: Profile Books
Fischer, E.P./Wiegandt, K. (2010) Evolution und Kultur des Menschen. Frankfurt: Fischer
Fischer, J. (2012) Affengesellschaft, Frankfurt: Suhrkamp
Fitch, W.T. (2005) The evolution of language: a comparative
view. In: Biology and Philosophy 20, 193-230
*Foley, W.A.(1997) Anthropological Linguistics. Oxford: Blackwell
Fouts, R. / Mills, S.T. (2000) Unsere nächsten Verwandten. München:
Droemer/Knaur [engagiert; wie Schimpansen die Zeichensprache der Gehörlosen
lernen]
Fouts, R. S. / Fouts, D. H. (1999) Chimpanzee sign language
research. In P. Dolhinow / A. Fuentes (eds.) The nonhuman
primates. Neurological Research, 23, 787-794.
Fouts, R.S. / Waters, G. (2001) Chimpanzee sign language and
Darwinian continuity: Evidence for a neurology continuity of
language.
Fouts, R.S., Jensvold, M.L.A. / Fouts, D.H. (2002). Chimpanzee
signing: Darwinian realities and Cartesian delusions. In M. Bekoff,
C. Allen / G. Burghardt (eds.) The cognitive animal: Empirical
and theoretical perspectives in animal cognition. Cambridge,
MA: MIT Press, pp. 285-291
Fouts, R. Jensvold, M.L., / Fouts, D. (2004) Talking chimpanzees.
In Bekoff, M.(ed.) Encyclopedia of animal behavior. Greenwood
Publishing Group.
R.A. Gardner/B.-T. Gardner (1979) Ein Affe lernt die Zeichensprache.
In: H. Leuninger/M.H.Miller/F. Müller (eds.) Linguistik und Psychologie.
Bd. 2. Frankfurt: Athenäum Fischer, 3-30.
* R.A. Gardner/B.-T. Gardner/Th.E. Van Catfort (eds.)(1989) Teaching
Sign Language to Chimpanzees. New York: Sate University of New York Press
*Goodall, J. (1986) The Chimpanzees of Gombe: Patterns
of Behavior. Cambridge: Belknap Press/Harvard University Press. [Pionierarbeit:
Schimpansen bauen sich Werkzeuge, geben Kultur weiter]
S. Greenspan/S.S. Shanker (2007) Der erste Gedanke. Frühkindliche Kommunikation und die Evolution menschlichen Denkens. Weinheim: Beltz
*H. Y. Hu, L. He, K. Fominykh, Z. Yan, S. Guo, X. Zhang, M. S. Taylor, L. Tang, J. Li, J. Liu, W. Wang, H. Yu & Ph. Khaitovich (2012) Evolution of the human-specific microRNA miR-941 In: Nature Communications 3, 23 October 2012
Hauser, M.T. (2001) Wilde Intelligenz. Was Tiere wirklich denken.
München: Beck
*Hauser, M.T./Chomsky, N./Fitch, W.T. (2002) The Faculty of Language: What
is it, who has it, and how did it evolve? In: Science 298, 1596-1579 [Evolution
und die Chomsky-Theorie]
Zu Hauser aktuell: New York Times vom 20.8.2010 sowie den aktualisierten Wikipedia-Artikel
Hayes, K.J. and Nissen, C.H.
(1971) Higher mental funcitons of a home-raised chimpanzee. In: Schrier,
A.M. and Stollnitz, F. (eds). Behaviour of Non-human Primates, Vol. 4, New
York: Academic Press, 50-115.
Herman, L. M. / Richards, D. G. / Wolz, J. P. (1984). Comprehension
of sentences by bottlenosed dolphins. Cognition, 16-129.
Herrmann,C.S./Pauen, M./Rieger, J.W. Schicktanz (eds.)(2005) Bewusstsein. Philosophie-Neurowissenschaften-Ethik.
München: Fink (UTB)
Hobaiter, C./Poisot, T./Zuberbühler/ Hoppitt,W./ Gruber, W.
(2014) Social Network Analysis Shows Direct Evidence for Social Transmission
of Tool Use in Wild Chimpanzees. In: PLOS
Biology September 30, 2014
* Hockett, Ch.F.
(1960) The origin of speech. In: Scientific American,
203, 88-96 (dt. in: Schwidetzky, I. (Hg.)(1973) Über
die Evolution der Sprache. Anatomie, Verhaltensforschung,
Sprachwissenschaft, Anthropologie. Frankfurt: Fischer,
135-169)
Hoffmann, L. /Leimbrink, K. / Quasthoff,
U. (Hg.)(2011) Die Matrix der menschlichen Entwicklung.
Berlin/Boston: de Gruyter
*Huber, L. (2021) Das rationale Tier. Berlin: Suhrkamp
Hurford, J.R./Studder-Kennedy, M./Knight, C. (eds.) (1998) Approaches to the Evolution of Language. Cambridge: University Press
Hurford, J. R. (2007) The Origins of Meaning. Oxford: University Press
Hurford, J. R. (2011) The Origins of Grammar.
Oxford: University Press
Jensvold, M.L.A.
(2000). A review of Apes, Language, and the Human Mind. Journal of Sociolinguistics,
4, 277-281
Kappeler, P.M.-/van Schaik, C. (2005) Cooperation in Primates and Humans.
Mechanisms and Evolution. Berlin: Springer
Kellogg, W.N. and Kellogg, L.A. (1968)
The ape and the child: a study of environmental influence upon early behavior.
New York: Whittlesey House.
King, B.J. (2004) The Dynamic Dance. Nonvocal Communication in African Great
Apes. New York: Harvard University Press.
*Krohs, U./Toepfer, G. (Hg.)(2005) Philosophie der Biologie. Frankfurt: Suhrkamp
Kulturwissenschaftliches
Institut (Hg.) Jahrbuch 2002/2003. Essen
Kulturwissenschaftliches Institut (Hg.) Jahrbuch 2003. Bielefeld: transcript
N. Lee/L. Mikesell/A.D. Joaquin/A.W. Mates, J.H. Schumann (2009) The Interactional Instinct. Oxford: University Press
G. Lewis-Kraus, G. (2019) Is Ancient DNA Research Revealing New Truths — or Falling Into Old Traps" In: NYT-Magazine
*Lieberman, P. (2006) Toward
an Evolutionary Biology of Language. Harvard: University Press
Lock, A. / Peters, Ch.R. (1996) Handbook of Human Symbolic Evolution. Oxford:
University Press
D. Lohmar (2016) Denken ohne Sprache. Phänomenologie des nicht-sprachlichen Denkens bei Mensch und Tier im Licht der Evolutionsforschung, Primatologie und Neurologie. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer Verlag
Macneilage, P. (2008)
The Origin of Speech. Oxford: University Press
*Mayr, E. (2003) Das ist Evolution. München: Bertelsmann [bedeutender
Evolutionsbiologe gibt Überblick]
McCrone, J. (1991) The Ape That Spoke. Language and the Evolution of the Human
Mind. New York: Avon Books
*McGrew, W./Marchant, L.F./Nishida, T. (eds.) (1996) Great Ape Societies. Cambridge: University Press [wichtige Beiträge zur Kultur von Affen]
*McGrew, W. (2004) The
Cultured Chimpanzee: Reflections on Cultural Primatology. Cambridge: University
Press [state of the art]
McNeill, D. (ed.)(2000) Language and gesture. Cambridge: University Press.
[zur Gebärdensprache]
Mesoudi, A., Whiten, A. and Laland, K. N. (2004). Is human cultural evolution Darwinian? Evidence reviewed from the perspective of 'The Origin of Species'. Evolution, 58 (1), 1-11

*Nagel, T. (1974) What is
it like to be a bat. In: Philosophical Review 83, 435-450 [wichtiger
philosoph. Artikel]
Napier, J.R./Napier, P.H. (1994) The Natural History of the Primates. Cambridge:
MIT Press
*Pauen, M. (2007) Was ist
der Mensch? Stuttgart: dva [Determinismus etc.]
Paul, A. (1998) Von Affen und Menschen. Darmstadt: Wiss. Buchgesellschaft.
Pepperberg, I. M. (1983). Cognition in the African Grey parrot: Preliminary
evidence for auditory/vocal comprehension of the class concept. Animal Learning
and Behavior, 11, 179-185
Pepperberg, M.I. (2009) Alex und ich. Die einzigartige Freundschaft
zwischen einer Harvard-Forscherin und dem schlausten Vogel der Welt. München: mvg-Verlag
*Perler, D. / Wild, M. (Hg.)(2005) Der Geist der Tiere. Frankfurt: Suhrkamp
(stw 1741) [anspruchsvolle Texte zur Diskussion]
Pinker, Steven/Jackendoff, R.(2005) The faculty of language: what’s special about it? Cognition 95, 201-236
Plessner, H. (2018/1961) Philosophische Anthropologie. Göttinger Vorlesung vom Sommersemester 1961. Herausgegeben von Julia Gruevska, Hans-Ulrich Lessing und Kevin Liggieri. Berlin: Suhrkamp [Klassiker der Anthropologie]
*Pollard, K. (2009) Der feine Unterschied. In: Spektrum der Wissenschaft Juli, 56-62 [genetische Unterschiede Mensch-Schimpanse]
Premack, D./Woodruff, G. (1978) Does the chimpanzee have a ‘theory of mind’? In: Behavioral and Brain Sciences 1, 515-526
Premack, D. / Premack, A.J. (1983) The Mind of an Ape. New York: W.W. Norton
Reich, D. (2018) Who we are and how we got
there. New York: Pantheon Books
Roberts, W. (1998) Principles of animal cognition. Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill.
Schusterman / Krieger
*Röska-Hardy, L. S./Neumann-Held, E.M. (eds) (2008) Learning
from Animals? Examining the Nature of Human Uniqueness. New York: Psychology
Press
Roth, G. (2010) Wie einzigartig ist der Mensch? Die lange Evolution der Gehirne
und des Geistes. Heidelberg: Spektrum
Rowlands, M. (2010) Der Philosoph und der Wolf. München: Piper
Sampson, G./Gil, D./Trudgill, P. (2009) Language Complexity as an Evolving Variable. Oxford: University Press
Savage-Rumbaugh, S.
/ Lewin, R. (1998) Kanzi – der sprechende Schimpanse.
München: Knaur [(1994) Kanzi, the Ape At the Brink of the Human Mind.
New York: John Wiley & Sons]
Savage-Rumbaugh,
S. et al. (1993) Language Comprehension in ape and child. Monographs of the
Society for Research in Child Development 58 (3-4).
*Schmid, H.B./Schweikard, D.P. (2009)(Hg.) Kollektive
Intentionalität:
Eine Debatte über die Grundlagen des
Sozialen. Frankfurt: Suhrkamp [auch zur Diskussion des Tomasello-Ansatzes]
*Searle, J.R. (2006) Geist. Frankfurt: Surkamp [Einführung in die Philosophie des Geistes]
Sebeok, T.A./Umiker-Sebeok,
J. (1980) Speaking of Apes: A Critical Anthology of Two-Way Communication
with Man. New York: Plenum Press
*Sitte, P. (Hg.)(1999) Jahrhundertwissenschaft Biologie. München:
Beck
Sommer, V. (2007/2) Darwinisch denken: Horizonte in der Evolutionsbiologie. Stuttgart: Hirzel
Sommer, V. (2008) Schimpansenland: Wildes Leben in Afrika. München: Beck
Steinig, W. (2006) Als die Wörter tanzen lernten. Ursprung und Gegenwart von Sprache. Heidelberg: Spektrum
Strecker, B. (1987)
Strategien des kommunikativen Handelns. Düsseldorf: Schwann
*Tallerman, M./Ginson, K.R. (eds)(2012) The Oxford Handbook of Language Evolution. Oxford: University Press
Tembrock, G. (1996) Akustische Kommunikation bei Säugetieren. Die Stimmen der Säugetiere und ihre Bedeutung. Darmstadt: Wiss. Buchgesellschaft
Tennie, C. / Call, J. / Tomasello, M. (2012). Untrained Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii) Fail to Imitate Novel Actions. PLoS ONE. 7, e41548.
Terrace, H.S., Petitto, L.A., Sanders, R.J. / Bever, T.G. (1979). Can an ape
create a sentence? Science, 206, 891-902.
[skeptische Sicht des syntaktischen Vermögens von Affen]
The Chimpanzee Sequencing and Analysis Consortium (2005) Initial Sequence of the Chimpanzee Genome and Com-parison with the Human Genome. In: Nature 437, 69-87
Tintemann, U. (Hg.)(2009) "Der Mensch ist Mensch nur durch die
Sprache". Zur Sprachlichkeit des Menschen. Paderborn: Fink
*Tomasello, M. (2002) Die kulturelle Entwicklung des menschlichen Denkens.
Frankfurt: Suhrkamp
*Tomasello, M./Rakoczy, H. (2003) What makes Human Cognition Unique? Form Individual
to Shared Collective Intentionality. In: Mind & Language 18.2, 121-147
*Tomasello, M. (2009) Die Ursprünge der menschlichen Kommunikation. Frankfurt: Suhrkamp
Tomasello, M. (2010) Warum wir kooperieren. Frankfurt: Suhrkamp
*Tomasello, M. (2014) Eine Naturgeschichte des menschlichen Denkens. Frankfurt: Suhrkamp [Orig. (2014) bei Harvard UP]
Thomasello, M. (2016) Eine Naturgeschichte der menschlichen Moral. Berlin: Suhrkamp
*Tomasello, M. (2020) Mensch werden - Eine
Theorie der Ontogenese. Berlin: Suhrkamp
Vauclair, J. (1996) Animal cognition. Cambridge, Massachusetts:
Harvard University Press
Vauclair, J. (2004) Lateralization of communicative signals in nonhuman primates
and the hypothesis of the gestural origin of language. In: Interaction Studies
5:3, 365-386
Wallman, J. (1992) Aping Language. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
de Waal, F. (2002) Der Affe und der Sushimeister. München: Hanser [Kulturweitergabe
durch Affen]
de Waal, F. (2009) Der Affe in uns:
Warum wir sind, wie wir sind. München: dtv
Whiten, A. (ed.) (1991) Natural Theories of Mind. Oxford: Basil
Blackwell
Whiten, A. (1996) Imitation, Pretence and Mindreading: Secondary
Representation in Comparative Primatology and Developmental Psychology.
In: Russon, A./Bard, K.A./Parker, S.T. (eds). Reaching Into Thought:
The Minds of the Great Apes. Cambridge University Press, 300-324
Whiten, A. Horner, V. and Marshall-Pescini, S (2003). Cultural Panthropology.
Evolutionary Anthropology, 12, 92-105
Whiten, A., Horner, V.,
Litchfield, C. and Marshall-Pescini, S. (2004). How do apes ape? Learning
and Behaviour 32, 36-52
Wider, H.T./de Luce, J. (eds.)(1983) Language in Primates. Berlin: Springer.
Wieser, W. (1998) Die
Erfindung der Individualität oder Die zwei Gesichter der Evolution.
Heidelberg: Spektrum
Links
Charles Hockett (Spezifika menschl. Sprache)
Seite des Chimpanzee
and Human Communication Institute (Washington), das Roger Fouts (s.o.)
gegründet hat und Publikationen
des Instituts
Interview mit Prof. Savage-Rumbaugh
Deutsches Primatenzentrum, Göttingen
Schimpansen und Gedächtnis (Film) Dazu: Spiegel Online
Schimpansen imitieren nicht... Tennie/Call/Tomasello 2013
Imitiation (MPI)
Können
Tiere denken? (Arte-Doku)
Affen & Sprache
Gorilla Foundation ("Koko"-Projekt)
- Konversation
mit dem Gorilla Koko
Center for
Great Ape
Savage-Rumbaugh
(Kanzi)
Jane-Goodall-Institute
Primaten-Netz
Interview mit William McGrew
Homepage Volker Sommer
Friends
of Washoe
Fossey Gorilla Fund
Homepage Marc
D. Hauser / CEL
Homepage Dan Sperber (Modularität,
Evolution, Kultur, Relevanz) (viele Aufsätze als pdf)
Gehirn-Atlas
Dietmar
Todt: Wie verständigen sich
die Primaten? (pdf)(FU Berlin)
Dietmar Todt: Akustische Kommunikation (pdf)(FU Berlin)
